The Importance of Energy in Manufacturing and in Policy
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has brought energy policy into focus across the world starting with Germany. During the most recent geopolitical tensions, Russia has shut down the Nord Stream 1 pipeline for maintenance. This has sent gas prices soaring, with immediate effects on Germany who is reliant on Russian gas for 35-55% of its gas imports. Energy is a key input into industrial production and Germany remains an industrial powerhouse, but there isn’t much depth of reporting on the issue. The Financial Times and Reuters have started to cover the issue through surveys of German industrial businesses. According to these surveys, roughly “one in ten companies had curtailed or interrupted production due to the price jumps.” If the conflict continues, industrial businesses will exhibit more stress when winter comes and energy demand rises further.
Over at kyla’s Newsletter, she explains how energy is intertwined with the crypto economy. It is a good preview for next week when Exponential Industry will go deeper into energy policy and its relationship to industrial and manufacturing businesses.
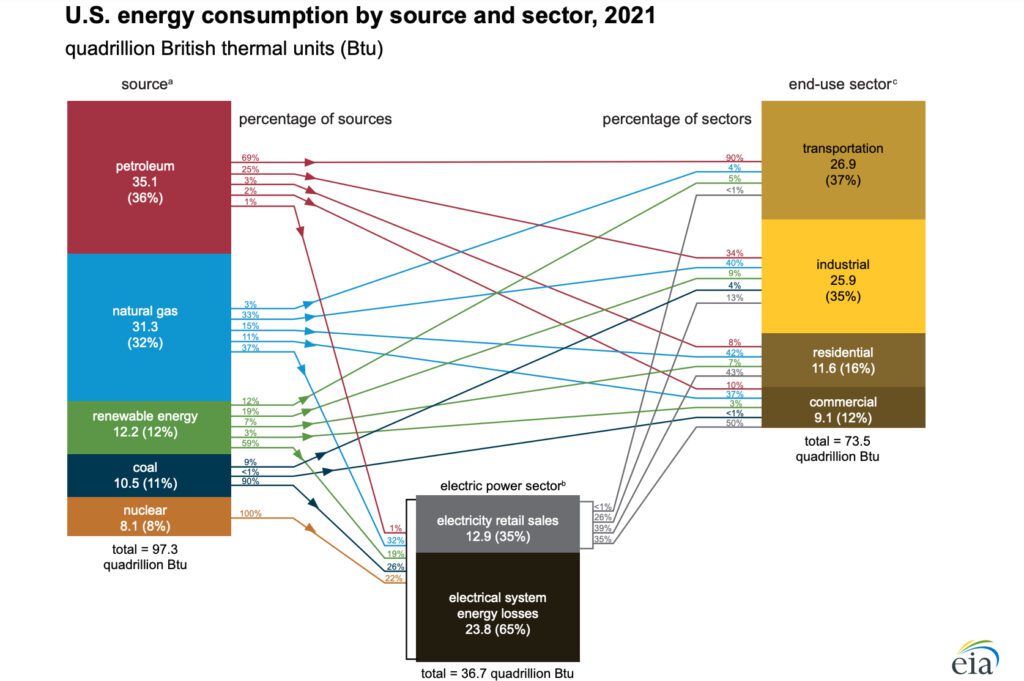
For starters, in the United States industrial sector end-use accounts for a third of all energy consumption.
Assembly Line
Capturing this week's trending industry 4.0 and emerging industrial technology media
Sustainability in Aerospace Composites Manufacturing: How AI and IIoT Drive Results
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency defines sustainable manufacturing as the creation of products in a manner that takes environmental factors into consideration and actively seeks to minimize negative impacts while saving on energy and natural resources. Sustainable manufacturing also enhances employee, community and product safety. Naturally, AI and IIoT are leveraged in the composite manufacturing industry in order to enhance material savings, reduce waste and increase throughput while minimizing energy consumption.
Our Industrial Life: S. 2 Ep. 4 - How digitization is decarbonizing industry
Change Management: Data Collaboration for AI-Enabled Factories
AI prescriptions that optimize production are fueled by data factories already own. They are also based on processes with which manufacturers are intimate. For high-impact digital transformation, industrial AI specialists initiate and sustain collaborative relationships with subject matter experts (SMEs). These relationships foster mutual learning. Committed collaboration and knowledge sharing empowers manufacturers to integrate data-driven decision-making on the shop floor. In the process, they also develop the digital maturity mindset so critical to flourishing during manufacturing’s great technological reset.
Within a broader universal digital ecosystem, plant engineers, manufacturing executives, managers, and operators must forge their own path. At the level of production, this path harnesses computational thinking (i.e., to optimize processes continually with state-of-the-art technology. The best manufacturing leaders do this in a spirit of collaboration and continuous learning with AI specialists.
For Industry 4.0 to succeed, manufacturing education must transform
Released today, Transforming Manufacturing Education: The Path to Train the Industry 4.0 Workforce offers perspectives from both industry and academia that help identify the future workflows and skills needed for mechanical engineers, manufacturing engineers, and CNC machinist roles over the next decade.
In the next decade, the manufacturing industry will continue to undergo notable changes through digital transformation and role convergence. While the three roles we analyzed will evolve differently over time, our research showed academia and industry agreed on the rising importance of design for manufacturing (DfM), artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI and ML) across these roles. Impressively, 90% of survey respondents agreed that growing students’ DfM knowledge and skills was the most impactful way for academia to develop the future manufacturing workforce
Computer whizz making sense of supply chain puzzles
Keelvar’s artificial intelligence-driven software products — oversimplifying it greatly — help businesses gain “richer information” from their suppliers, Holland says, so they can avoid waste, cut down on costs and make often opaque auction processes more efficient. “You can then start to piece together multiple suppliers” like “a big complex jigsaw puzzle,” he says, matching buyers with a supplier or multiple suppliers as an insurance policy against mishaps.
It is this puzzle that Holland has been piecing together since he was a teenager. Starting his career in a dairy company in west Cork, Holland’s father “went out on his own”, he says, setting up a small family chemicals company. “While we were in school, he set up that company so we kind of witnessed company formation, start-up days in the 1980s, an era where there was no such thing as venture capital,” he says.
Multi-objective optimization of recycling and remanufacturing supply chain logistics network with scalable facility under uncertainty
Recycling and remanufacturing logistics network affects the scale and efficiency of sustainable development of the manufacturing industry. This paper designs a multi-level closed-loop supply chain network with supplier, manufacturer, recycling centers, preprocessing centers and processing centers. An improved nonlinear grey Bernoulli-Markov model is developed to predict the recycled quantity. The capacity of recycling center and preprocessing center, the demand of manufacturer and the inventory of preprocessing center are formulated as constraints. A dynamic multi-objective model, which is based on scalable logistics facilities, takes into account the minimization of system operating costs and minimization of time costs related to the out-of-stock and inventory in each operating cycle. This model realizes the dynamic selection of the scale of facilities. Objective weighted genetic algorithm is adopted to transform multi-objective optimization problem into a single-objective. A scrap automobile products calculations are analyzed to verify the effectiveness and practicability of this model.
Capital Expenditure
Tracking this week's major mergers, partnerships, and funding events in manufacturing and supply chain
Varjo Raises $40 Million Series D Funding to Build a True-to-Life, Industrial Metaverse
Backed by EQT Ventures, Atomico, Volvo Car Tech Fund, Lifeline Ventures, and new strategic investors Mirabaud and Foxconn, the new capital will enable Varjo to build a true-to-life, industrial metaverse for all professionals. Varjo will use the funds for its R&D cloud services, namely Varjo Reality Cloud, the company’s XR streaming platform that was announced in April. The new capital will help the company continue to scale its software and hardware offerings across new enterprise verticals such as design & manufacturing, engineering, education, and healthcare.
Realtime Robotics Announces Additional Funding of $14.4 Million
Realtime Robotics, the leader in collision-free autonomous motion planning for industrial robots, today announced that it has secured $14.4 million in additional funding, with Soundproof Ventures, Heroic Ventures and SIP Global Partners as lead investors. The funding comes on the heels of the official launch of the company’s new RapidPlan software, which helps manufacturers design and deploy industrial automation faster and more efficiently. With RapidPlan, customers can automate the programming, deployment and control of their industrial robots within applications such as automotive or logistics, autonomously creating and choreographing all robot movements without the need for brand-specific robot programming.
ELISE Raises €14.5 million to scale Connected Engineering
We are incredibly proud to announce that we have closed our Series A financing round of €14.5 million! The investment is led by the renowned US Investor Spark Capital, with participation from BMW i Ventures, Cherry Ventures, UVC Partners, and Venture Stars. “This new investment will allow us to make significant progress towards our goal of becoming the low-code standard in engineering. The ease of use of our visual programming language enables engineers to model and automate development processes in the shortest possible time,” explained Moritz Maier, co-founder and CEO of ELISE. “With our open platform, we enable engineers to transfer the agile and efficient methods of software development to hardware development. This automates manual and repetitive tasks and enables companies to manage the growing complexity of product development in the face of increasing cost and innovation pressure.”
Hitachi Acquires Key Industry 4.0 Systems Integrator – Flexware Innovation
Hitachi, Ltd. announced that it acquired Flexware Innovation, Inc. which has been a leading manufacturing Systems Integrator (SI) since 1996. Flexware Innovation was a strategic acquisition for Hitachi due to its focus on the TOTAL SEAMLESS SOLUTION that links “shop floor” and “top floor” with data and digital technology.
With this acquisition of Flexware Innovation, Hitachi will strengthen and enhance its business in the domain of MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), Software Development, Business Intelligence (BI), and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) implementation capabilities in North America, and accelerate the digitalization with JR Automation which engages in the robotic SI & automation. Further, through cooperation with Hitachi Vantara which has expertise in building and deploying Enterprise and Cloud applications, Hitachi will be able to provide TOTAL SEAMLESS SOLUTION from robotic SI & automation, MES, SCADA, BI, and ERP and help manufacturing leaders increase corporate value.
SLM and Nikon enter into Investment Agreement – Nikon to launch public takeover offer for SLM
SLM Solutions Group AG (“SLM Solutions”, “SLM” or the “Company”) and Nikon Corporation (“Nikon”) have entered into an Investment Agreement in relation to a voluntary public takeover offer that Nikon intends to launch for all outstanding shares of SLM at a cash consideration of EUR 20 per share.
With SLM becoming part of Nikon’s digital manufacturing strategy, SLM management is convinced this transaction will further enhance SLM’s ability to stay at the forefront of metal Additive Manufacturing and enhance its leadership position in delivering superior products and solutions to its customers.
Amazon is buying Cloostermans, a mechatronics specialist in Belgium, to ramp up its robotics operations
Amazon has made a string of startup acquisitions over the years to build out its robotics business; now, the e-commerce leviathan is taking an interesting turn in that strategy as it expands its industrial warehouse capabilities. Amazon is acquiring Cloostermans, a company out of Belgium that is a specialist in mechatronics. It’s been building technology to move and stack heavy palettes and totes, and robotics used to package products for customer orders. Amazon has been using those products as a customer of Cloostermans’ since 2019 for e-commerce operations; it’s making the acquisition to ramp up its R&D and deployment in that area.
